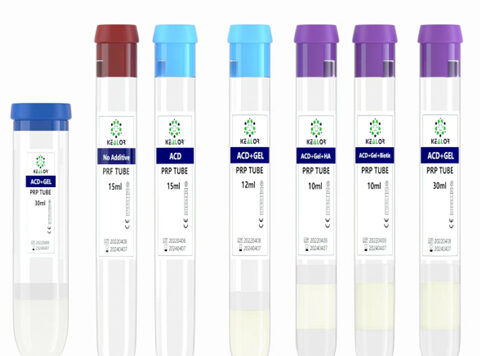
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a blood product that is widely used in regenerative medicine and orthopedic treatments. PRP is obtained by centrifuging whole blood, resulting in a concentrated suspension of platelets and growth factors. In addition to an anticoagulant, several chemicals can be used during the preparation of PRP to enhance its therapeutic properties. In this article, we will discuss the chemicals used for preparing PRP, except for the anticoagulant.
Calcium Chloride (CaCl2)
Calcium chloride is a chemical compound that is commonly used in the preparation of PRP. It is added to PRP to activate platelets and enhance the release of growth factors. The addition of calcium chloride can also increase the viscosity of PRP, making it easier to handle during injection.
Thrombin
Thrombin is a clotting factor that plays a crucial role in the formation of blood clots. It can also be used to activate platelets and initiate the release of growth factors in PRP. Thrombin can be added to PRP in the form of a commercially available thrombin gel or solution.
Collagen
Collagen is a protein that is a major component of the extracellular matrix of many tissues, including bone and cartilage. It can be added to PRP to enhance its regenerative properties and promote tissue repair. Collagen can be incorporated into PRP in the form of a gel or scaffold.
Hyaluronic Acid (HA)
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring polysaccharide that is found in many tissues, including synovial fluid and cartilage. It is commonly used in the treatment of osteoarthritis and can be added to PRP to enhance its lubricating properties and improve joint mobility. Hyaluronic acid can be incorporated into PRP in the form of a gel or solution.
Platelet Activating Factor (PAF)
Platelet activating factor is a lipid molecule that can be found in many tissues, including platelets. It plays a key role in the regulation of platelet activation and can be added to PRP to enhance its therapeutic properties. PAF can be incorporated into PRP in the form of a solution.
Conclusion
In addition to an anticoagulant, several chemicals can be used during the preparation of PRP to enhance its therapeutic properties. Calcium chloride, thrombin, collagen, hyaluronic acid, and platelet activating factor are commonly used to activate platelets, enhance the release of growth factors, and promote tissue repair. The use of these chemicals in PRP preparation can be tailored to the specific clinical application and can provide a safe and effective treatment option for patients with a wide range of conditions.