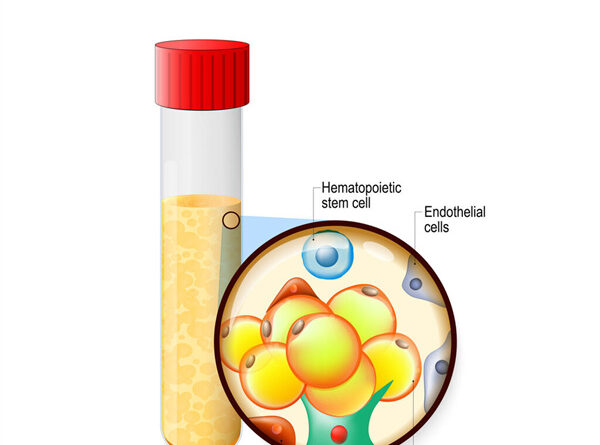
Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that is commonly performed after a mastectomy, a surgical procedure that removes one or both breasts due to cancer or other medical conditions. Autologous breast reconstruction involves using a woman’s own tissue, usually from the abdomen or buttocks, to reconstruct the breast. Fat grafting, or lipo filling, is a technique used in autologous breast reconstruction that involves transferring a patient’s own fat from one part of the body to the breast to improve the shape and volume.
Fat grafting in autologous breast reconstruction has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its natural results and the lack of implant-related complications. One of the major advantages of fat grafting is that it does not involve the use of foreign material, which can be a source of complications such as infection, rupture, and implant migration.
However, fat grafting is not always suitable for all patients, particularly those with limited donor site availability or a lack of excess body fat. Additionally, the success of fat grafting depends on various factors such as the patient’s age, the quality and quantity of the fat, and the technique used.
In autologous breast reconstruction, fat grafting is often used in combination with other techniques such as flap reconstruction or tissue expansion. The procedure involves harvesting fat from the patient’s abdomen or thighs using liposuction. The harvested fat is then processed and purified to remove excess fluids, blood, and oil.
Once the fat is prepared, it is injected into the breast using a small needle or cannula. The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, and patients may experience mild discomfort and swelling for a few days following the procedure. Multiple sessions may be required to achieve the desired results.
Although fat grafting is generally safe, it is not without risks. Complications may include infection, asymmetry, contour irregularities, and loss of fat graft volume over time. In rare cases, fat necrosis, or the death of fat cells, may occur.
Overall, fat grafting in autologous breast reconstruction can be a safe and effective option for certain patients. However, it is important for patients to have a thorough discussion with their surgeon about the risks and benefits of the procedure and to have realistic expectations about the outcomes.