Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy has gained popularity in recent years as a non-surgical treatment option for various conditions, including erectile dysfunction and female sexual dysfunction. PRP contains a high concentration of platelets, growth factors, and cytokines that can promote tissue healing and regeneration. The O shot and P shot are PRP therapies that target female and male sexual dysfunction, respectively. However, some patients and practitioners may wonder whether PRP used for these therapies can contain red blood cells and buffy coat. In this blog, we will explore the question, “Can platelet-rich plasma contain red blood cells and buffy coat for O shot and P shot?”
What is the O Shot and P Shot?
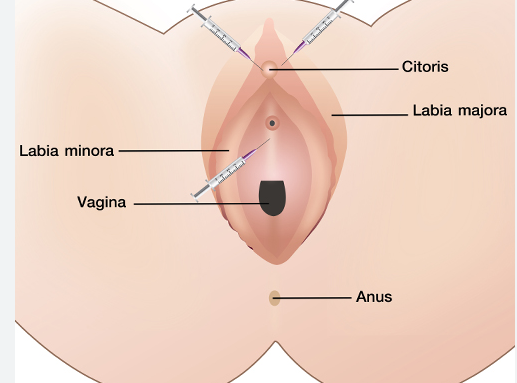
The O Shot and P Shot are two PRP therapies that target female and male sexual dysfunction, respectively. The O Shot involves injecting PRP into the clitoris and the vaginal wall, while the P Shot involves injecting PRP into the penis. These therapies aim to improve sexual function, increase sensitivity, and enhance pleasure by promoting tissue regeneration and blood flow.
Can PRP Contain Red Blood Cells and Buffy Coat?
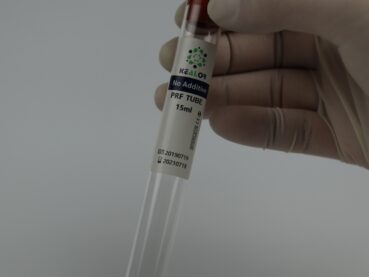
PRP is typically prepared using a centrifugation process that separates the blood components based on their density. During the centrifugation process, the heavier components, such as red blood cells and platelets, settle to the bottom of the tube, while the lighter components, such as plasma, remain at the top.
While PRP is primarily composed of platelets, it can contain small amounts of red blood cells and buffy coat, which is a layer of white blood cells and platelets that sits between the red blood cells and plasma. However, the presence of red blood cells and buffy coat in PRP can affect its quality and efficacy.
Red blood cells can release hemoglobin, which can decrease the effectiveness of PRP by scavenging the growth factors and reducing their bioavailability. Additionally, buffy coat can contain high levels of leukocytes, which can trigger an inflammatory response and reduce the therapeutic effects of PRP.
Therefore, to ensure the highest quality and efficacy of PRP, it is essential to use a standardized PRP preparation protocol that minimizes the presence of red blood cells and buffy coat.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the O Shot and P Shot are PRP therapies that can improve sexual function by promoting tissue regeneration and blood flow. While PRP can contain small amounts of red blood cells and buffy coat, it is crucial to minimize their presence to ensure the highest quality and efficacy of PRP. Therefore, practitioners must use a standardized PRP preparation protocol that separates the blood components effectively and removes any unwanted cellular components before administering PRP for the O Shot or P Shot.